What is gut health?
This is probably not the first time hearing “gut health.” In the digestive tract, gut health refers to the balance of microorganisms. It is crucial to take good care of the gut and preserve the right balance of these microorganisms to maintain good physical and mental health and a robust immune system.
The gut is the system responsible for breaking down food into the nutrients our bodies use to function. From the esophagus to the bowel, gut health includes the digestive system. The different parts of the gut perform various functions, and other bacteria colonies break food down into digestible forms.

Why is it essential to maintain a healthy gut?
The truth is that gut health plays a crucial role in our overall health, with increasing evidence demonstrating that a healthy gut microbiome can improve your mental well-being and immune response.
When the gut wall is healthy, it acts as a barrier, preventing viruses, fungi, and ‘bad’ bacteria from entering the bloodstream. There are times when this barrier becomes permeable, otherwise known as a leaky gut, allowing these nasties to enter and make us sick.
Is there a connection between the gut and the brain?
The brain has a direct impact on the stomach and intestines. For instance, just thinking about eating can make the stomach release its juices before the food arrives. This connection goes both ways.
These two organs are physically and biochemically connected in many different ways. Communication between the gut and brain is made possible by the gut-brain axis.
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication network that links the enteric and central nervous systems. This network is not only anatomical; it includes endocrine, humoral, metabolic, and immune routes of communication as well. The autonomic nervous system, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and nerves within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract all link the gut and the brain. This allows the brain to influence intestinal activities, including the movement of functional immune effector cells, while the microbiome affects mood, cognition, and mental health.
How are the gut and brain connected?
A.Vagus Nerve and the Nervous System
Neurons are the cells in the brain and central nervous system that control your body’s behavior. An estimated 100 billion neurons are found in the human brain, and five hundred million neurons in your gut communicate with your brain via nerves in your nervous system.
One of the largest nerves in the body connects the gut to the brain, known as the vagus nerve. Signals are sent in both directions, and the vagus nerve interconnects the gut-brain axis and stress.
B. Neurotransmitters
Chemicals called neurotransmitters also connect your gut and brain.
A neurotransmitter called serotonin contributes to feelings of happiness and regulates the body’s internal clock.
Neurotransmitters control emotions and feelings in the brain. The trillions of microbes in your gut also produce many neurotransmitters. Serotonin is primarily produced in the stomach, and your gut microbes also produce a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which helps control feelings of anxiety and fear.
C. Microbes in the gut produce other chemicals that affect the brain.
Trillions of microbes in your gut also produce chemicals that affect the brain’s function. Gut microbes produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). SCFAs are a type of fatty acid that microbes in the gut produce when they break down dietary fiber.
SCFAs can influence behavior and mood by changing the way nerve cells in the brain communicate with each other. SCFAs are produced when gut microbes break down dietary fiber, affecting brain function in many ways, such as reducing appetite.
D. Gut Microbes and Inflammation
Your gut and gut microbes are responsible for controlling what is passed into and excreted from your body, which affects your immune system and inflammation. Several brain disorders like depression and Alzheimer’s can be triggered by the immune system being too active for too long. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an inflammatory toxin made by certain bacteria, and it can cause inflammation if too much of it passes from the gut into the blood.
Bacteria and LPS can enter the bloodstream when the gut barrier becomes leaky.
Several brain disorders, such as severe depression, dementia, and schizophrenia, are associated with inflammation and high levels of LPS in the blood.
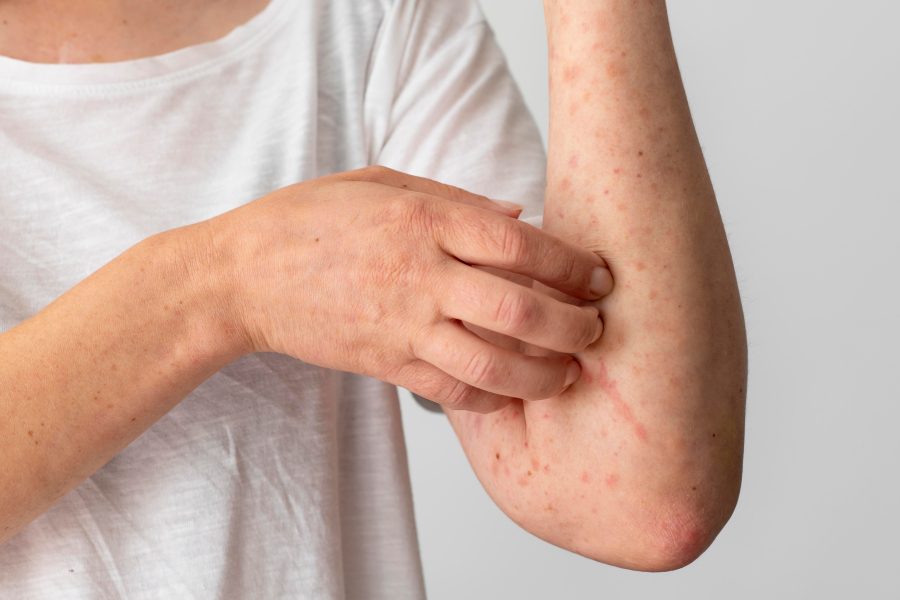
What are the signs that you have a gut imbalance?
- Digestive issues like bloating, constipation, or diarrhea
- Skin problems like eczema or psoriasis
- Mood swings or brain fog
- Sleep issues | Fatigue
- Autoimmune diseases
- Unintentional weight changes
- Food intolerances
What are the leading causes of gut imbalance?
- Antibiotics
- Poor diet | High sugar diet
- Stress
- Environmental toxins
- Birth control pills
- Chronic illnesses
How do you heal your gut with diet?
- Eat fiber-rich foods, such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- Eat fermented foods, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut.
- Eat probiotic-rich foods, such as miso, tempeh, and kimchi.
- Avoid processed foods, sugar, and artificial sweeteners.
- Drink plenty of water.
There has been a shift in global dietary patterns towards a greater dependence on unhealthy, heavily processed foods that have been linked to a higher likelihood of developing mental disorders. On the other hand, a diet rich in nutrients is believed to have protective effects on mental health, and researchers are now investigating the biological mechanisms that underlie this connection. One possible mediator of this link is the gut microbiota, which is known to be influenced by both diet and mental health.

What is the importance of probiotics and prebiotics in healing our gut?
Your health should improve by implementing both probiotics and prebiotics into your diet. However, they have different roles:
Probiotics. Probiotics, such as foods or supplements, are live bacteria that benefit our health, mainly in the digestive system. Probiotics have several health benefits, including improved digestion, reduced risk of colon cancer, and improved mental health.
Probiotic foods
Foods high in prebiotic
- Asparagus
- Dandelion greens
- Garlic
- Leeks
- Onions
- Legumes, beans, and peas
- Oats
- Bananas
- Berries
- Honey
How do digestive enzymes help gut bacteria?
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in the body. Enzymes can be found in all body tissues, including the liver, pancreas, and muscles. Some enzymes are responsible for digesting food, while others help to protect the body from disease. Enzymes are also involved in the production of energy and the metabolism of nutrients.
Digestive enzymes help gut bacteria to break down food, absorb nutrients, and protect the gut from infection and disease. Enzymes can help to improve digestion, increase energy levels, and boost the immune system. Enzymes may also help to reduce the risk of some chronic diseases, such as heart disease.
It is common for people to confuse enzymes and probiotics. The good bacteria in your gut are made up of probiotics, and you need them to keep your digestive tract healthy. Unlike enzymes, probiotics are not capable of breaking down or digesting food.

What lifestyle changes can help heal your gut?
Digest your food efficiently
Reduce your levels of stress
- Meditating
- Walking
- Massage
- Spending time with family or friends
- Essential oil diffusion
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Laughing
- Interacting with a pet
Ensure you get enough sleep
Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated
Change your diet
Exercise regularly
Consume fiber-rich and probiotic-rich foods
Fiber is a plant-based nutrient that lowers the risk of metabolic diseases by promoting the growth and variety of good bacteria in the gut.
Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha, are also highly regarded for their gut-boosting properties due to the presence of probiotics. Yogurt, in particular, may aid in the relief of gastrointestinal conditions such as diarrhea, inflammatory bowel disease, and constipation.
Foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut can benefit the microbiome by improving its function, decreasing the abundance of disease-causing bacteria in the intestines, and promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacilli.
The connection between your teeth and gut
Consider adding a supplement
Probiotic supplements are becoming more popular as awareness of the importance of digestive health grows. While probiotic supplements are not a cure-all for gut health, there is some evidence that they can boost the microbiota and restore gut health under certain conditions.
Here are some supplements we recommend:
RestorFlora – This combination of probiotic yeast and bacteria offers comprehensive digestive flora support with an advanced, dual-action approach to maintain a healthy intestinal environment.
Omni Biotic AB 10 Probiotic – Omni-Biotic AB 10 is a probiotic supplement specifically developed to restore and maintain gut microbiome diversity.
Omni Biotic Balance Probiotic – Omni-Biotic Balance is a probiotic supplement for the immune system that was specifically developed to provide successful immune support for the gut.
Omni Biotic Stress Release Probiotic – Omni-Biotic Stress Release is a probiotic supplement specifically developed to support the gut-brain axis and promote the body’s resilience during stress.
*Please check with your healthcare provider before taking these.
Consume alcohol in moderation
Repeated alcohol consumption has been linked to gastritis, a condition in which the gut becomes inflamed. Heartburn, chronic discomfort, ulcers, and bacterial infections can all result from such inflammation.
Excessive drinking is also associated with intestinal inflammation, a sign of an unhealthy gut. According to research, this type of inflammation alters the microbiota, including how well it functions and can throw it off balance.

How can you test for gut imbalance?
There are numerous methods for detecting gut imbalance, and some tests are more reliable than others, but the main thing is to find a test that works for you.
A stool test is the most common method for testing gut imbalance. This test can detect the presence of harmful bacteria and yeast in the gastrointestinal tract, and it can also reveal the number of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Another way to test for gut imbalance is through a breath test. This test measures the levels of hydrogen and methane in the breath that the gut bacteria produces.
A food intolerance test can also identify an intestinal imbalance. This test evaluates the body’s reaction to different foods.
Working with a highly trained Functional Medicine Practitioner is the best way to test for gut imbalance. They can advise you on the best test for you and interpret the results.
What can be done to treat gut imbalance?
- Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria that can aid in the restoration of the gut’s balance of good and bad bacteria.
- Diet changes: Making dietary changes, such as avoiding processed foods and increasing fiber consumption, can help improve gut health.
- Exercise: Exercise can help promote gut health by boosting immunity and increasing blood flow to the gut.
- Stress management: Stress management can aid in the reduction of inflammation in the gut, which can lead to imbalance.
What long-term effects might a gut imbalance have?
- Autoimmune diseases
- Digestive disorders
- Hormonal imbalances
- Mood disorders
- Skin problems
- Sleep disorders
If you are experiencing any of these health issues, it is worth looking into whether a gut imbalance is to blame.
Following these tips on how to heal your gut can lead to a healthier and happier life. Paying attention to what you eat and drink can make a big difference in your gut health. Adding probiotics and prebiotics into your daily life can give your gut the good bacteria it needs to function effortlessly. Finally, don’t forget to reduce stress in your life, as it can impact gut health negatively. Take some time for yourself, relax, and heal your gut! If you are seeking support, book a consultation with Dr. Truc our Functional Medicine Practitioner.
FAQ’s
1. How can I improve my gut health?
Eat more fiber, add fermented foods like yogurt or kimchi, limit processed and fatty foods, alcohol, and caffeine. Keep active, sleep well, and manage stress to boost good gut bacteria.
2. What is gut health?
Gut health means having a balanced digestive system and microbes that help digest food, absorb nutrients, support immunity, and good mental health. A healthy gut prevents digestion problems and maintains overall wellness.
3. What are the symptoms of an unhealthy gut?
Symptoms include bloating, constipation, diarrhea, gas, fatigue, frequent sickness, and mood changes like anxiety. If these are persistent, your gut health might be out of balance.
4. How can I detox my gut?
Drink plenty of water daily, eat fiber-rich and alkaline foods, stay active, and add probiotics. These steps help your gut flush out toxins and maintain a healthy microbiome.
5. How can I “reset” my gut?
To reset your gut, eat a high-fiber, diverse, and minimally processed diet, include fermented foods, reduce added sugars, drink water, exercise, and manage stress for a healthier digestive system.

