That is because your thyroid gland is a small body organ in the shape of a butterfly that controls the metabolism of your body. When this gland synthesizes an excessive amount of thyroid hormone, you are afflicted with hyperthyroidism. This disorder speeds up practically every system in your body, producing the symptoms that can appear gradually and are occasionally even confused with stress, aging, or other health issues.
The early detection of hyperthyroidism will help in effective diagnosis and treatment at the initial stage to avoid complications. The majority have gone through months or years with the symptoms, only to correlate them with dysfunctions of the thyroid. Information may ensure that you are aware of what to watch in order to seek appropriate medical attention when the need arises.
This guide expounds on the first symptoms that most individuals experience, and what to do in case you believe you have thyroid complications.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a situation in which your thyroid gland secretes too much of thyroid hormones, mainly thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones regulate the metabolism, cardiac rhythm, body temperature, and energy production. With extreme levels, normal levels make your body processes proceed at a rate higher than expected.
The disease is prevalent among 1.2 percent of the U.S. population, with a five to ten times higher chance of development of hyperthyroidism in women than men. It can begin at any age, but normally begins between 20 and 40.
Hyperthyroidism is the opposite of hypothyroidism, in which the thyroid glands produce an excessive amount of hormone. Hypothyroidism decreases body processes, whereas hyperthyroidism accelerates the same. These two are health issues that require care to cure and affect your body in opposite ways.
The degree of hyperthyroidism is different. Others have mild symptoms accumulating gradually, and others have the severe ones accumulating rapidly. Unattended hyperthyroidism is subject to severe complications such as heart-related complications, loss of bone, and the life-threatening condition known as thyroid storm.
Want to understand the difference between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism more clearly? Both conditions affect the thyroid but in completely opposite ways. To learn how they differ in symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment, read our detailed guide here: Hypothyroidism vs Hyperthyroidism Explained
What is the Cause of Hyperthyroidism?

There are several diseases that cause excessive production of hormones in your thyroid. The knowledge of hyperthyroidism is useful in determining the risk factors and prescribing treatment.
The most prevalent cause is Graves’ disease, which causes 60 to 80 percent of hyperthyroidism cases. It is an autoimmune disorder, and this triggers your body into creating antibodies, which consequently causes the thyroid gland to overproduce hormones. Graves’ disease is familial and affects women more than it affects men.
Thyroid nodules could be secretory of excess hormone in unregulated amounts by the thyroid. These lumps of the thyroid gland secrete thyroid hormone without the positive feedback of the body.
Transient hyperthyroidism may be caused by thyroiditis or inflammation of the thyroid gland. The leakage of hormones in the blood is a transient overload once the thyroid is inflamed. This normally comes after childbirth or after viral infections.
Too much iodine may cause hyperthyroidism in those who are prone to it. The hormones are produced through the requirement of iodine, which overproduces them. Some of the sources contain some form of medicine, supplements, and contrast dye, which are applied in medical imaging.
Drugs that contain thyroid hormone may lead to hyperthyroidism when they are taken in excess. Those using thyroid replacement in the treatment of hypothyroidism are at risk of developing hyperthyroidism when their dosage should be changed.
What are the Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism impacts a variety of body systems, forming a constellation of symptoms of different severities and combinations.
- One of the key symptoms that can be observed is the loss of weight, which cannot be explained by the normal level or even an increased appetite. More calories are burned than you consume because of your increased metabolism. You can lose 10 to 20 pounds and more without effort at all.
- The excess thyroid hormone overstimulates your cardiovascular system and results in palpitations or a rapid and irregular heartbeat. Your heart will either be racing, pounding, or skipping. There is a possibility that others end up with atrial fibrillation, an irregular heartbeat that exposes them to stroke.
- You dislike hot weather in which other individuals are comfortable. You may be extremely sweaty in cool weather and like cold weather.
- Tremor is particularly in your hands, which is a result of overstimulation of your nervous system. There is also the sensation of shaking when you are holding something in your hands, writing, or stretching your arms.
- Your mental state is undergoing hyperthyroidism, which makes you nervous, anxious, and irritable. You are either nervous or find it very difficult to relax, or maybe you have moods. The usual problems are problems with concentration and racing thoughts.
- The fact that more energy is being burned and yet fatigue and muscular weakness are a contradiction seems to be a general symptom. Muscles may be weak, particularly in your upper arms and thighs.
- Sleep disturbances entail the inability to sleep, sleeping too early or too late, or feeling that one has not slept enough despite getting enough sleep. Your hyperactive metabolism and nervousness disrupt the normal sleeping patterns.
- Bowel movements or diarrhea are also enhanced by the high rate of digestion. Increased bowel movements can occur as opposed to normal or loose stools.
- Women with hyperthyroidism experience changes in their menstrual patterns. The intervals may be less common, less neurotic, or discontinued.
- Eye alterations exist in persons, particularly those with Graves’ disease. Eyes may be observed to be swollen, gritty/irritable, or sensitive to light.
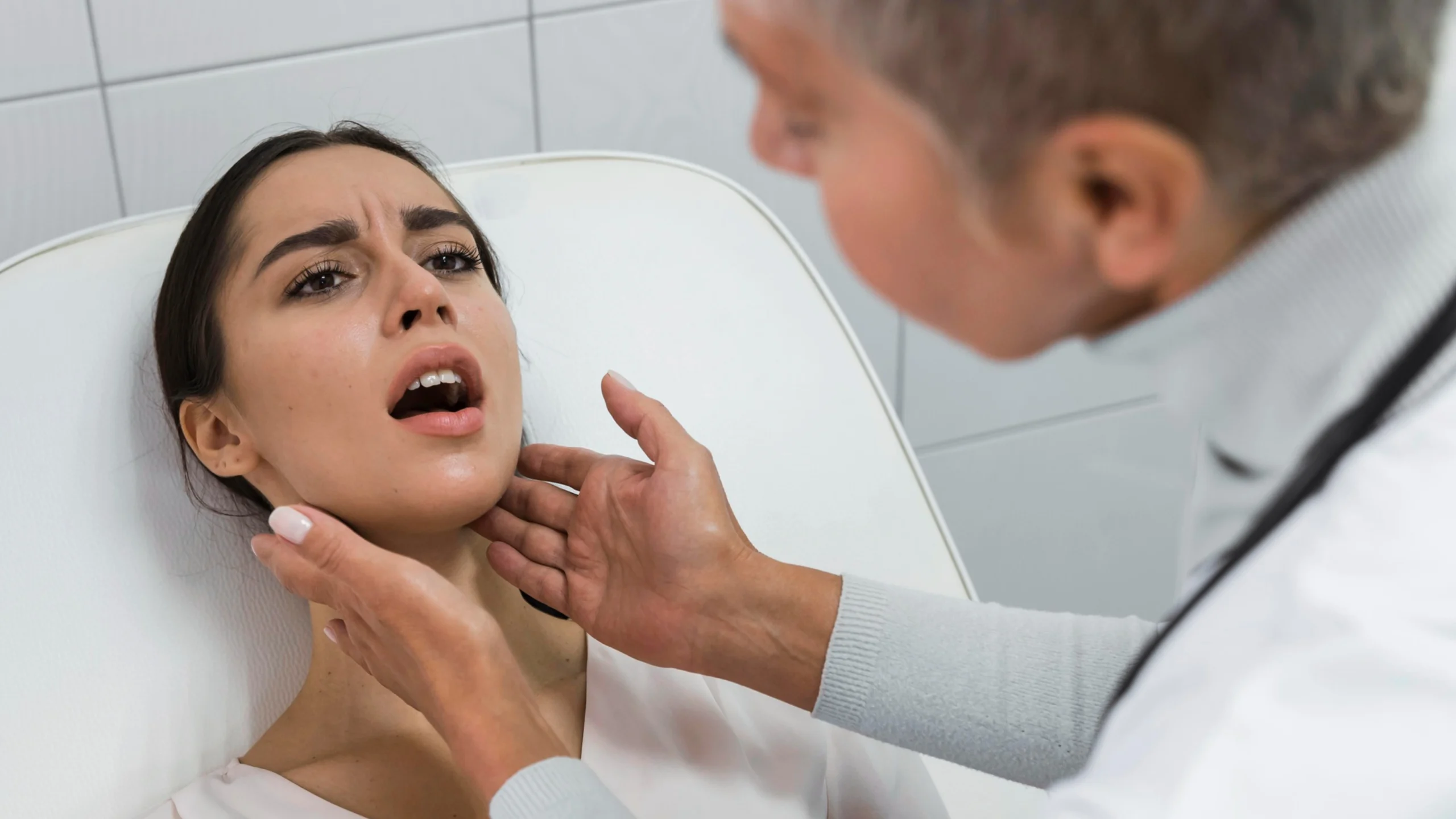
- A goiter refers to an enlarged thyroid gland (therefore, it looks like a swelling in the neck, at its base). The gland may become soft, or it may be hard to swallow.
What Are the Signs of Hyperthyroidism?

However, the symptoms are what you feel, and the signs are what the medical practitioner perceives when he/she examines. Having knowledge of hyperthyroidism symptoms aids in the diagnosis of the condition.
- Among the most predictable ones is tachycardia or rapid heart rate. You can have a pulse rate of over 100 beats per minute. Doctors are able to detect abnormal rates of the heartbeat either in an examination or an electrocardiogram.
- One of the common symptoms would be a noticeable tremor in your extended hands. When you open your arms and squeeze your fingers, it is difficult to hide the shaking. The symptom helps the physician to ascertain the implications of the nervous system.
- Skin is moist and warm because of the higher rate of blood supply and perspiration. Examining yourself, you can tell that your skin is rather warmer and damper than normal. This is contrary to the cold, dry skin of hypothyroidism.
- Enlargement of the thyroid or goiter is normally palpable or visible. As a physician will observe, you might have swelling at the bottom of your neck, or you might have a big gland that could also be inspected during the examination. Either the enlargement is diffuse or nodular.
- In my eyes, some of the symptoms are lid retraction, whereby the eyelids of the upper eye will be drawn in, leaving you with a bigger portion of the white part of your eye. It leads to this effect of staring. Graves’ disease may lead to exophthalmos, causing protruding eyes.
- The scenario of having doctors check on knee or ankle reflexes is hyperreflexia or exaggerated reflexes. The reflexes are exaggerated and faster than normal, which is why it is an over-stimulated nervous system.
- Weight loss, despite the appearance of the eating process being normal, is manifested. Although you may not have said it, friends, family members, or doctors may notice that you have lost weight.
- Extreme cases occur in muscle wasting, and this is mainly in the shoulders and thighs. Physical will reveal that doctors will have decreased muscle bulk.
- Onycholysis, or separation of nails and nail bed, and between nails and nail bed, also takes place in a limited number of people. This effect is not so common, but it is the systemic effects of excess thyroid hormone.
How is Hyperthyroidism Diagnosed?
The proper diagnosis entails the clinical examination and the lab examination. Knowing what was involved in the process of a hyperthyroidism test would enable you to be aware of what to expect.
Medical history and physical examination constitute the initial part of the diagnostic process. The doctor will ask about the symptoms, family history, drugs, and exposure to iodine. Physical examination entails inspection of swelling of the thyroid gland, heart rate and rhythm, shaking, and eye inspection.
The significant diagnostic test is blood tests, as they identify the amount of thyroid hormones. TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) is the first test that has to be ordered. There is low or undetectable TSH, which indicates hyperthyroidism. It takes the levels of Free T4 and free T3 to make sure that the production of excess thyroid hormone is present.
Thyroid antibody tests are used in the detection of autoimmune causes. A sign of TSI (thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin) is Graves ‘ disease. These examinations help in the determination of the cause of the condition and treatment options.
The radioactive uptake test is a thyroid examination of the level of uptake of iodine. Growth of uptake will be a sign of either toxic nodules or Graves’ disease. Reduced uptake is an indication of thyroiditis.
Thyroid scan: This is a procedure whereby images of your thyroid are produced by the use of radioactive tracers. The scan will show whether the entire gland is over-secreting or the presence of some nodules, which might be secreting an excess of hormone.
What is the Treatment of Hyperthyroidism?
The way hyperthyroidism is treated is dependent on the cause, the degree of the condition, age, and general well-being. There are a number of successful treatment options for hyperthyroidism.
The thyroid hormone production is suppressed by anti-thyroid drugs like propylthiouracil or methimazole. These medications suppress the thyroid’s ability to use iodine in making hormones. The duration of treatment is 12 months to 18 months.
Radioiodine therapy is used to destroy the cells in the thyroid glands that produce an excess amount of hormone. Radioactive iodine is administered in the form of a tablet and is accumulated in the thyroid gland. The radiation kills the overgrowth of thyroid tissue in a few weeks or months.
Beta-blockers are not a direct treatment of hyperthyroidism, but can help to control the symptoms in addition to other therapies. These medicines influence the heart rate, reduce tremors, and reduce anxiety.
Thyroid surgery entails the excision of a portion or the whole thyroid gland. It is also operated in the event of failure of medication, radioactive iodine is contraindicated, or we have large goiters that cause symptoms.
How and When to Call a Medical Professional?
Visit the doctor in case of any symptoms or signs of hyperthyroidism. By early diagnosis and treatment, complications are prevented.
Seek medical attention when the loss of weight cannot be explained, the rapid heartbeat, excessive sweating, tremors, and anxiety occur. Thyroid function testing should be done through these symptoms.
Treatment should be sought in case of acute dyspnea of acute and sharp nature, chest pain, or fainting as an emergency. These symptoms may be an indication of serious cardiovascular conditions.
Women with an infertile or irregular menstrual cycle are encouraged to discuss thyroid tests with their health care provider.
Conclusion
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism early include unexplained weight loss, increased heart rate, excessive sweating, shaking, anxiety, and sleepiness.
The symptoms that will be detected are tachycardia, which can be observed through tremor that is warm and moist, as well as increased thyroid function.
Women are able to notice the changes that occur during menstruation, but men may exhibit sexual dysfunction.
Blood tests allow early diagnosis and detection of the symptoms of gonorrhea. Hyperthyroidism is treated using drugs, radioactive iodine, or surgery. They can have normal thyroid functioning with proper treatment of the majority of them.
Conscious Medicine will be providing complete functional and integrative care of thyroid diseases in the entire metro Atlanta area. Dr. Truc Nguyen is a physician with over 15 years of experience who works with the cause of thyroid dysfunction.
Contact Conscious Medicine is a virtual doctor delivering you a chance to discover how our root-cause approach can empower you to achieve lasting thyroid balance and optimal health. Book a virtual consultation with us today.